|
Scribus
Open source desktop publishing at your fingertips
|
|
Scribus
Open source desktop publishing at your fingertips
|
Typedefs | |
| typedef Point | BezierCurve[] |
| typedef double | Coord |
| typedef std::vector< Crossing > | Crossings |
| typedef std::vector< CrossingNode > | CrossingGraph |
| typedef std::vector< Crossings > | CrossingSet |
| typedef SimpleCrosser | DefaultCrosser |
| typedef BezierCurve< 1 > | LineSegment |
| typedef BezierCurve< 2 > | QuadraticBezier |
| typedef BezierCurve< 3 > | CubicBezier |
| typedef long | ICoord |
| typedef std::vector< Region > | Regions |
| typedef std::back_insert_iterator< std::vector< Path > > | iter |
Functions | |
| double | deg_to_rad (double deg) |
| double | rad_to_deg (double rad) |
| std::vector< std::pair< double, double > > | find_intersections (vector< Geom::Point > const &A, vector< Geom::Point > const &B) |
| std::vector< std::pair< double, double > > | find_self_intersections (OldBezier const &Sb) |
| std::vector< std::pair< double, double > > | find_self_intersections (D2< SBasis > const &A) |
| bool | intersect_BB (OldBezier a, OldBezier b) |
| void | recursively_intersect (OldBezier a, double t0, double t1, int deptha, OldBezier b, double u0, double u1, int depthb, std::vector< std::pair< double, double > > ¶meters) |
| double | log4 (double x) |
| double | Lmax (Point p) |
| unsigned | wangs_theorem (OldBezier a) |
| std::vector< std::pair< double, double > > | find_intersections (D2< SBasis > const &A, D2< SBasis > const &B) |
| std::vector< std::pair< double, double > > | find_intersections (std::vector< Point > const &A, std::vector< Point > const &B) |
| std::vector< std::pair< double, double > > | find_self_intersections (std::vector< Point > const &A) |
| SBasis | bezier_to_sbasis (Coord const *handles, unsigned order) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< SBasis > | handles_to_sbasis (T const &handles, unsigned order) |
| int | bezier_fit_cubic (Point *bezier, Point const *data, int len, double error) |
| int | bezier_fit_cubic_r (Point bezier[], Point const data[], int const len, double const error, unsigned const max_beziers) |
| int | bezier_fit_cubic_full (Point bezier[], int split_points[], Point const data[], int const len, Point const &tHat1, Point const &tHat2, double const error, unsigned const max_beziers) |
| Point | bezier_pt (unsigned const degree, Point const V[], double const t) |
| Point | darray_left_tangent (Point const d[], unsigned const len) |
| Point | darray_left_tangent (Point const d[], unsigned const len, double const tolerance_sq) |
| Point | darray_right_tangent (Point const d[], unsigned const len, double const tolerance_sq) |
| int | bezier_fit_cubic (Point bezier[], Point const data[], int len, double error) |
| Coord | subdivideArr (Coord t, Coord const *v, Coord *left, Coord *right, unsigned order) |
| Bezier | operator+ (const Bezier &a, double v) |
| Bezier | operator- (const Bezier &a, double v) |
| Bezier | operator* (const Bezier &a, double v) |
| Bezier | operator/ (const Bezier &a, double v) |
| Bezier | reverse (const Bezier &a) |
| Bezier | portion (const Bezier &a, double from, double to) |
| std::vector< Point > | bezier_points (const D2< Bezier > &a) |
| Bezier | derivative (const Bezier &a) |
| Bezier | integral (const Bezier &a) |
| Interval | bounds_fast (Bezier const &b) |
| Interval | bounds_exact (Bezier const &b) |
| Interval | bounds_local (Bezier const &b, Interval i) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out_file, const Bezier &b) |
| int | circle_circle_intersection (Point X0, double r0, Point X1, double r1, Point &p0, Point &p1) |
| template<typename T > | |
| T | portion (const T &t, const Interval &i) |
| double | SignedTriangleArea (Point p0, Point p1, Point p2) |
| int | mod (int i, int l) |
| pair< map< int, int >, map< int, int > > | bridges (ConvexHull a, ConvexHull b) |
| std::vector< Point > | bridge_points (ConvexHull a, ConvexHull b) |
| unsigned | find_bottom_right (ConvexHull const &a) |
| ConvexHull | sweepline_intersection (ConvexHull const &a, ConvexHull const &b) |
| ConvexHull | intersection (ConvexHull a, ConvexHull b) |
| ConvexHull | merge (ConvexHull a, ConvexHull b) |
| ConvexHull | graham_merge (ConvexHull a, ConvexHull b) |
| bool | intersectp (ConvexHull a, ConvexHull b) |
| template<class T > | |
| ConvexHull | operator* (ConvexHull const &p, T const &m) |
| bool | are_near (Coord a, Coord b, double eps=EPSILON) |
| double | wrap_dist (double from, double to, double size, bool rev) |
| CrossingGraph | create_crossing_graph (std::vector< Path > const &p, Crossings const &crs) |
| void | merge_crossings (Crossings &a, Crossings &b, unsigned i) |
| void | offset_crossings (Crossings &cr, double a, double b) |
| Crossings | reverse_ta (Crossings const &cr, std::vector< double > max) |
| Crossings | reverse_tb (Crossings const &cr, unsigned split, std::vector< double > max) |
| CrossingSet | reverse_ta (CrossingSet const &cr, unsigned split, std::vector< double > max) |
| CrossingSet | reverse_tb (CrossingSet const &cr, unsigned split, std::vector< double > max) |
| void | clean (Crossings &cr_a, Crossings &cr_b) |
| template<typename C > | |
| std::vector< Rect > | bounds (C const &a) |
| void | sort_crossings (Crossings &cr, unsigned ix) |
| SBasis | L2 (D2< SBasis > const &a, unsigned k) |
| D2< SBasis > | multiply (Linear const &a, D2< SBasis > const &b) |
| D2< SBasis > | multiply (SBasis const &a, D2< SBasis > const &b) |
| D2< SBasis > | truncate (D2< SBasis > const &a, unsigned terms) |
| unsigned | sbasis_size (D2< SBasis > const &a) |
| double | tail_error (D2< SBasis > const &a, unsigned tail) |
| Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > | sectionize (D2< Piecewise< SBasis > > const &a) |
| D2< Piecewise< SBasis > > | make_cuts_independant (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &a) |
| Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > | rot90 (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &M) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | dot (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &a, Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &b) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | cross (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &a, Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &b) |
| Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > | operator* (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &a, Matrix const &m) |
| Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > | force_continuity (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &f, double tol, bool closed) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | reverse (const D2< T > &a) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | portion (const D2< T > &a, Coord f, Coord t) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | operator== (D2< T > const &a, D2< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | operator!= (D2< T > const &a, D2< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | are_near (D2< T > const &a, D2< T > const &b, double tol) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator+ (D2< T > const &a, D2< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator- (D2< T > const &a, D2< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator+= (D2< T > &a, D2< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator-= (D2< T > &a, D2< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator- (D2< T > const &a) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator* (D2< T > const &a, Point const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator/ (D2< T > const &a, Point const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator*= (D2< T > &a, Point const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator/= (D2< T > &a, Point const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator* (D2< T > const &a, double b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator*= (D2< T > &a, double b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator/ (D2< T > const &a, double b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator/= (D2< T > &a, double b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator* (D2< T > const &v, Matrix const &m) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator+ (D2< T > const &a, Point b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator- (D2< T > const &a, Point b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator+= (D2< T > &a, Point b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | operator-= (D2< T > &a, Point b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| T | dot (D2< T > const &a, D2< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| T | cross (D2< T > const &a, D2< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | rot90 (D2< T > const &a) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | compose (D2< T > const &a, T const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | compose_each (D2< T > const &a, D2< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | compose_each (T const &a, D2< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | derivative (D2< T > const &a) |
| template<typename T > | |
| D2< T > | integral (D2< T > const &a) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Rect | bounds_fast (const D2< T > &a) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Rect | bounds_exact (const D2< T > &a) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Rect | bounds_local (const D2< T > &a, const Interval &t) |
| IntersectorKind | line_intersection (Geom::Point const &n0, double const d0, Geom::Point const &n1, double const d1, Geom::Point &result) |
| int | intersector_ccw (const Geom::Point &p0, const Geom::Point &p1, const Geom::Point &p2) |
| IntersectorKind | segment_intersect (Geom::Point const &p00, Geom::Point const &p01, Geom::Point const &p10, Geom::Point const &p11, Geom::Point &result) |
| IntersectorKind | line_twopoint_intersect (Geom::Point const &p00, Geom::Point const &p01, Geom::Point const &p10, Geom::Point const &p11, Geom::Point &result) |
| int | centroid (std::vector< Geom::Point > p, Geom::Point ¢roid, double &area) |
| Interval | operator+ (const Interval &a, const Interval &b) |
| Interval | operator- (const Interval &a, const Interval &b) |
| Interval | operator+= (Interval &a, const Interval &b) |
| Interval | operator-= (Interval &a, const Interval &b) |
| Interval | operator* (const Interval &a, const Interval &b) |
| Interval | operator*= (Interval &a, const Interval &b) |
| Interval | unify (const Interval &a, const Interval &b) |
| boost::optional< Interval > | intersect (const Interval &a, const Interval &b) |
| double | lerp (double t, double a, double b) |
| Linear | reverse (Linear const &a) |
| Linear | operator+ (Linear const &a, Linear const &b) |
| Linear | operator- (Linear const &a, Linear const &b) |
| Linear & | operator+= (Linear &a, Linear const &b) |
| Linear & | operator-= (Linear &a, Linear const &b) |
| Linear | operator+ (Linear const &a, double b) |
| Linear | operator- (Linear const &a, double b) |
| Linear & | operator+= (Linear &a, double b) |
| Linear & | operator-= (Linear &a, double b) |
| bool | operator== (Linear const &a, Linear const &b) |
| bool | operator!= (Linear const &a, Linear const &b) |
| Linear | operator- (Linear const &a) |
| Linear | operator* (Linear const &a, double b) |
| Linear | operator/ (Linear const &a, double b) |
| Linear | operator*= (Linear &a, double b) |
| Linear | operator/= (Linear &a, double b) |
| Matrix | from_basis (Point const x_basis, Point const y_basis, Point const offset) |
| Matrix | operator* (Matrix const &m0, Matrix const &m1) |
| Matrix | elliptic_quadratic_form (Matrix const &m) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out_file, const Geom::Matrix &m) |
| Matrix | identity () |
| bool | operator== (Matrix const &a, Matrix const &b) |
| bool | operator!= (Matrix const &a, Matrix const &b) |
| int | winding (Path const &path, Point p) |
| bool | path_direction (Path const &p) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | append (T &a, T const &b) |
| bool | linear_intersect (Point A0, Point A1, Point B0, Point B1, double &tA, double &tB, double &det) |
| void | pair_intersect (Curve const &A, double Al, double Ah, Curve const &B, double Bl, double Bh, Crossings &ret, unsigned depth=0) |
| void | mono_pair (Path const &A, double Al, double Ah, Path const &B, double Bl, double Bh, Crossings &ret, double tol, unsigned depth=0) |
| std::vector< double > | curve_mono_splits (Curve const &d) |
| std::vector< double > | offset_doubles (std::vector< double > const &x, double offs) |
| std::vector< double > | path_mono_splits (Path const &p) |
| std::vector< std::vector< double > > | paths_mono_splits (std::vector< Path > const &ps) |
| std::vector< std::vector< Rect > > | split_bounds (std::vector< Path > const &p, std::vector< std::vector< double > > splits) |
| Crossings | curve_self_crossings (Curve const &a) |
| Crossings | self_crossings (Path const &p) |
| void | flip_crossings (Crossings &crs) |
| CrossingSet | crossings_among (std::vector< Path > const &p) |
| bool | contains (Path const &p, Point i, bool evenodd=true) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Crossings | curve_sweep (Path const &a, Path const &b) |
| Crossings | crossings (Path const &a, Path const &b) |
| CrossingSet | crossings (std::vector< Path > const &a, std::vector< Path > const &b) |
| template<typename iter > | |
| iter | inc (iter const &x, unsigned n) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | divide (Piecewise< SBasis > const &a, Piecewise< SBasis > const &b, unsigned k) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | divide (Piecewise< SBasis > const &a, Piecewise< SBasis > const &b, double tol, unsigned k, double zero) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | divide (Piecewise< SBasis > const &a, SBasis const &b, double tol, unsigned k, double zero) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | divide (SBasis const &a, Piecewise< SBasis > const &b, double tol, unsigned k, double zero) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | divide (SBasis const &a, SBasis const &b, double tol, unsigned k, double zero) |
| std::map< double, unsigned > | compose_pullback (std::vector< double > const &values, SBasis const &g) |
| int | compose_findSegIdx (std::map< double, unsigned >::iterator const &cut, std::map< double, unsigned >::iterator const &next, std::vector< double > const &levels, SBasis const &g) |
| std::vector< double > | roots (Piecewise< SBasis > const &f) |
| template<typename T > | |
| FragmentConcept< T >::BoundsType | bounds_fast (const Piecewise< T > &f) |
| template<typename T > | |
| FragmentConcept< T >::BoundsType | bounds_exact (const Piecewise< T > &f) |
| template<typename T > | |
| FragmentConcept< T >::BoundsType | bounds_local (const Piecewise< T > &f, const Interval &m) |
| template<typename T > | |
| T | elem_portion (const Piecewise< T > &a, unsigned i, double from, double to) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | partition (const Piecewise< T > &pw, std::vector< double > const &c) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | portion (const Piecewise< T > &pw, double from, double to) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | remove_short_cuts (Piecewise< T > const &f, double tol) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | remove_short_cuts_extending (Piecewise< T > const &f, double tol) |
| template<typename T > | |
| std::vector< double > | roots (const Piecewise< T > &pw) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator+ (Piecewise< T > const &a, typename T::output_type b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator- (Piecewise< T > const &a, typename T::output_type b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator+= (Piecewise< T > &a, typename T::output_type b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator-= (Piecewise< T > &a, typename T::output_type b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator- (Piecewise< T > const &a) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator* (Piecewise< T > const &a, double b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator/ (Piecewise< T > const &a, double b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator*= (Piecewise< T > &a, double b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator/= (Piecewise< T > &a, double b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator+ (Piecewise< T > const &a, Piecewise< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator- (Piecewise< T > const &a, Piecewise< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator+= (Piecewise< T > &a, Piecewise< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator-= (Piecewise< T > &a, Piecewise< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T1 , typename T2 > | |
| Piecewise< T2 > | operator* (Piecewise< T1 > const &a, Piecewise< T2 > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | operator*= (Piecewise< T > &a, Piecewise< T > const &b) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | compose (Piecewise< T > const &f, SBasis const &g) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | compose (Piecewise< T > const &f, Piecewise< SBasis > const &g) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | integral (Piecewise< T > const &a) |
| template<typename T > | |
| Piecewise< T > | derivative (Piecewise< T > const &a) |
| Coord | L1 (Point const &p) |
| Coord | LInfty (Point const &p) |
| bool | is_zero (Point const &p) |
| bool | is_unit_vector (Point const &p) |
| Coord | atan2 (Point const p) |
| Coord | angle_between (Point const a, Point const b) |
| Point | unit_vector (Point const &a) |
| Point | abs (Point const &b) |
| Point | operator* (Point const &v, Matrix const &m) |
| Point | operator/ (Point const &p, Matrix const &m) |
| Point | operator* (double const s, Point const &p) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out_file, const Geom::Point &in_pnt) |
| Point | operator^ (Point const &a, Point const &b) |
| bool | operator== (Point const &a, Point const &b) |
| bool | operator!= (Point const &a, Point const &b) |
| bool | operator<= (Point const &a, Point const &b) |
| Coord | L2 (Point const &p) |
| Coord | L2sq (Point const &p) |
| bool | are_near (Point const &a, Point const &b, double const eps=EPSILON) |
| Point | rot90 (Point const &p) |
| Point | lerp (double const t, Point const a, Point const b) |
| Coord | dot (Point const &a, Point const &b) |
| Coord | cross (Point const &a, Point const &b) |
| Coord | distance (Point const &a, Point const &b) |
| Coord | distanceSq (Point const &a, Point const &b) |
| unsigned | outer_index (Regions const &ps) |
| Regions | regions_from_paths (std::vector< Path > const &ps) |
| std::vector< Path > | paths_from_regions (Regions const &rs) |
| Regions | sanitize_path (Path const &p) |
| Regions | region_boolean (bool rev, Region const &a, Region const &b, Crossings const &cr) |
| Regions | region_boolean (bool rev, Region const &a, Region const &b, Crossings const &cr_a, Crossings const &cr_b) |
| Regions | region_boolean (bool rev, Region const &a, Region const &b) |
| SBasis | extract_u (SBasis2d const &a, double u) |
| SBasis | extract_v (SBasis2d const &a, double v) |
| SBasis | compose (Linear2d const &a, D2< SBasis > const &p) |
| SBasis | compose (SBasis2d const &fg, D2< SBasis > const &p) |
| D2< SBasis > | compose_each (D2< SBasis2d > const &fg, D2< SBasis > const &p) |
| Linear | extract_u (Linear2d const &a, double u) |
| Linear | extract_v (Linear2d const &a, double v) |
| Linear2d | operator- (Linear2d const &a) |
| Linear2d | operator+ (Linear2d const &a, Linear2d const &b) |
| Linear2d | operator- (Linear2d const &a, Linear2d const &b) |
| Linear2d & | operator+= (Linear2d &a, Linear2d const &b) |
| Linear2d & | operator-= (Linear2d &a, Linear2d const &b) |
| Linear2d & | operator*= (Linear2d &a, double b) |
| bool | operator== (Linear2d const &a, Linear2d const &b) |
| bool | operator!= (Linear2d const &a, Linear2d const &b) |
| Linear2d | operator* (double const a, Linear2d const &b) |
| SBasis2d | operator- (const SBasis2d &p) |
| SBasis2d | operator+ (const SBasis2d &a, const SBasis2d &b) |
| SBasis2d | operator- (const SBasis2d &a, const SBasis2d &b) |
| SBasis2d & | operator+= (SBasis2d &a, const Linear2d &b) |
| SBasis2d & | operator-= (SBasis2d &a, const Linear2d &b) |
| SBasis2d & | operator+= (SBasis2d &a, double b) |
| SBasis2d & | operator-= (SBasis2d &a, double b) |
| SBasis2d & | operator*= (SBasis2d &a, double b) |
| SBasis2d & | operator/= (SBasis2d &a, double b) |
| SBasis2d | operator* (double k, SBasis2d const &a) |
| SBasis2d | operator* (SBasis2d const &a, SBasis2d const &b) |
| SBasis2d | shift (SBasis2d const &a, int sh) |
| SBasis2d | shift (Linear2d const &a, int sh) |
| SBasis2d | truncate (SBasis2d const &a, unsigned terms) |
| SBasis2d | multiply (SBasis2d const &a, SBasis2d const &b) |
| SBasis2d | integral (SBasis2d const &c) |
| SBasis2d | derivative (SBasis2d const &a) |
| SBasis2d | sqrt (SBasis2d const &a, int k) |
| SBasis2d | reciprocal (Linear2d const &a, int k) |
| SBasis2d | divide (SBasis2d const &a, SBasis2d const &b, int k) |
| SBasis2d | compose (SBasis2d const &a, SBasis2d const &b) |
| SBasis2d | compose (SBasis2d const &a, SBasis2d const &b, unsigned k) |
| SBasis2d | inverse (SBasis2d const &a, int k) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out_file, const Linear2d &bo) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out_file, const SBasis2d &p) |
| Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > | cutAtRoots (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &M, double tol=1e-4) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | atan2 (D2< SBasis > const &vect, double tol=.01, unsigned order=3) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | atan2 (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > >const &vect, double tol=.01, unsigned order=3) |
| Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > | unitVector (D2< SBasis > const &vect, double tol=.01, unsigned order=3) |
| Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > | unitVector (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &vect, double tol=.01, unsigned order=3) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | curvature (D2< SBasis > const &M, double tol=.01) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | curvature (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &M, double tol=.01) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | arcLengthSb (D2< SBasis > const &M, double tol=.01) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | arcLengthSb (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &M, double tol=.01) |
| double | length (D2< SBasis > const &M, double tol=.01) |
| double | length (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &M, double tol=.01) |
| Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > | arc_length_parametrization (D2< SBasis > const &M, unsigned order=3, double tol=.01) |
| Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > | arc_length_parametrization (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &M, unsigned order=3, double tol=.01) |
| unsigned | centroid (Piecewise< D2< SBasis > > const &p, Point ¢roid, double &area) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | abs (SBasis const &f) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | abs (Piecewise< SBasis > const &f) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | max (SBasis const &f, SBasis const &g) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | max (Piecewise< SBasis > const &f, SBasis const &g) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | max (SBasis const &f, Piecewise< SBasis > const &g) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | max (Piecewise< SBasis > const &f, Piecewise< SBasis > const &g) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | min (SBasis const &f, SBasis const &g) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | min (Piecewise< SBasis > const &f, SBasis const &g) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | min (SBasis const &f, Piecewise< SBasis > const &g) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | min (Piecewise< SBasis > const &f, Piecewise< SBasis > const &g) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | signSb (SBasis const &f) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | signSb (Piecewise< SBasis > const &f) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | sqrt (SBasis const &f, double tol, int order) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | sqrt (Piecewise< SBasis > const &f, double tol, int order) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | sin (SBasis const &f, double tol, int order) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | sin (Piecewise< SBasis > const &f, double tol, int order) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | cos (Piecewise< SBasis > const &f, double tol, int order) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | cos (SBasis const &f, double tol, int order) |
| void | truncateResult (Piecewise< SBasis > &f, int order) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | reciprocalOnDomain (Interval range, double tol) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | reciprocal (SBasis const &f, double tol, int order) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | reciprocal (Piecewise< SBasis > const &f, double tol, int order) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | log (SBasis const &f, double tol=1e-3, int order=3) |
| Piecewise< SBasis > | log (Piecewise< SBasis >const &f, double tol=1e-3, int order=3) |
| SBasis | poly_to_sbasis (Poly const &p) |
| Poly | sbasis_to_poly (SBasis const &sb) |
| Interval | bounds_exact (SBasis const &a) |
| Interval | bounds_fast (const SBasis &sb, int order) |
| Interval | bounds_local (const SBasis &sb, const Interval &i, int order) |
| std::vector< std::vector< double > > | multi_roots (SBasis const &f, std::vector< double > const &levels, double htol, double vtol, double a, double b) |
| void | subdiv_sbasis (SBasis const &s, std::vector< double > &roots, double left, double right) |
| std::vector< double > | roots (SBasis const &s) |
| double | W (unsigned n, unsigned j, unsigned k) |
| Bezier | sbasis_to_bezier (SBasis const &B, unsigned q) |
| double | mopi (int i) |
| SBasis | bezier_to_sbasis (Bezier const &B) |
| std::vector< Geom::Point > | sbasis_to_bezier (D2< SBasis > const &B, unsigned qq) |
| void | build_from_sbasis (Geom::PathBuilder &pb, D2< SBasis > const &B, double tol) |
| Path | path_from_sbasis (D2< SBasis > const &B, double tol) |
| std::vector< Geom::Path > | path_from_piecewise (Geom::Piecewise< Geom::D2< Geom::SBasis > > const &B, double tol) |
| SBasis | operator+ (const SBasis &a, const SBasis &b) |
| SBasis | operator- (const SBasis &a, const SBasis &b) |
| SBasis & | operator+= (SBasis &a, const SBasis &b) |
| SBasis & | operator-= (SBasis &a, const SBasis &b) |
| SBasis | operator* (SBasis const &a, double k) |
| SBasis & | operator*= (SBasis &a, double b) |
| SBasis | shift (SBasis const &a, int sh) |
| SBasis | shift (Linear const &a, int sh) |
| SBasis | multiply (SBasis const &a, SBasis const &b) |
| SBasis | integral (SBasis const &c) |
| SBasis | derivative (SBasis const &a) |
| SBasis | sqrt (SBasis const &a, int k) |
| SBasis | reciprocal (Linear const &a, int k) |
| SBasis | divide (SBasis const &a, SBasis const &b, int k) |
| SBasis | compose (SBasis const &a, SBasis const &b) |
| SBasis | compose (SBasis const &a, SBasis const &b, unsigned k) |
| SBasis | inverse (SBasis a, int k) |
| SBasis | sin (Linear b, int k) |
| SBasis | cos (Linear bo, int k) |
| SBasis | compose_inverse (SBasis const &f, SBasis const &g, unsigned order, double zero) |
| SBasis | reverse (SBasis const &a) |
| SBasis | operator- (const SBasis &p) |
| SBasis | operator* (double k, SBasis const &a) |
| SBasis | operator/ (SBasis const &a, double k) |
| SBasis & | operator/= (SBasis &a, double b) |
| SBasis | operator+ (const SBasis &a, Linear const &b) |
| SBasis | operator- (const SBasis &a, Linear const &b) |
| SBasis & | operator+= (SBasis &a, const Linear &b) |
| SBasis & | operator-= (SBasis &a, const Linear &b) |
| SBasis | operator+ (const SBasis &a, double b) |
| SBasis | operator- (const SBasis &a, double b) |
| SBasis & | operator+= (SBasis &a, double b) |
| SBasis & | operator-= (SBasis &a, double b) |
| SBasis | truncate (SBasis const &a, unsigned terms) |
| SBasis | operator* (SBasis const &a, SBasis const &b) |
| SBasis & | operator*= (SBasis &a, SBasis const &b) |
| unsigned | valuation (SBasis const &a, double tol=0) |
| SBasis | portion (const SBasis &t, double from, double to) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out_file, const Linear &bo) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out_file, const SBasis &p) |
| void | first_false (std::vector< std::vector< bool > > visited, unsigned &i, unsigned &j) |
| unsigned | find_crossing (Crossings const &cr, Crossing x, unsigned i) |
| Shape | shape_boolean (bool rev, Shape const &a, Shape const &b, CrossingSet const &crs) |
| Shape | shape_boolean (bool rev, Shape const &a, Shape const &b) |
| std::vector< double > | region_sizes (Shape const &a) |
| Shape | shape_boolean_ra (bool rev, Shape const &a, Shape const &b, CrossingSet const &crs) |
| Shape | shape_boolean_rb (bool rev, Shape const &a, Shape const &b, CrossingSet const &crs) |
| Shape | boolop (Shape const &a, Shape const &b, unsigned flags, CrossingSet const &crs) |
| Shape | boolop (Shape const &a, Shape const &b, unsigned flags) |
| int | paths_winding (std::vector< Path > const &ps, Point p) |
| void | add_to_shape (Shape &s, Path const &p, bool fill) |
| int | inner_winding (Path const &p, std::vector< Path > const &ps) |
| double | fudgerize (double d, bool rev) |
| unsigned | pick_coincident (unsigned ix, unsigned jx, bool &rev, std::vector< Path > const &ps, CrossingSet const &crs) |
| unsigned | crossing_along (double t, unsigned ix, unsigned jx, bool dir, Crossings const &crs) |
| void | crossing_dual (unsigned &i, unsigned &j, CrossingSet const &crs) |
| void | outer_crossing (unsigned &ix, unsigned &jx, bool &dir, std::vector< Path > const &ps, CrossingSet const &crs) |
| std::vector< Path > | inner_sanitize (std::vector< Path > const &ps) |
| Shape | sanitize (std::vector< Path > const &ps) |
| Shape | stopgap_cleaner (std::vector< Path > const &ps) |
| CrossingSet | crossings_between (Shape const &a, Shape const &b) |
| Shape | boolop (Shape const &, Shape const &, unsigned flags, CrossingSet &) |
| std::vector< Path > | desanitize (Shape const &s) |
| void | find_bernstein_roots (double const *w, unsigned degree, std::vector< double > &solutions, unsigned depth, double left_t, double right_t) |
| unsigned | crossing_count (Geom::Point const *V, unsigned degree) |
| void | find_parametric_bezier_roots (Geom::Point const *w, unsigned degree, std::vector< double > &solutions, unsigned depth) |
| unsigned | crossing_count (double const *V, unsigned degree, double left_t, double right_t) |
| void | output (Curve const &curve, SVGPathSink &sink) |
| void | output (LineSegment const &curve, SVGPathSink &sink) |
| void | output (CubicBezier const &curve, SVGPathSink &sink) |
| void | output (QuadraticBezier const &curve, SVGPathSink &sink) |
| void | output (SVGEllipticalArc const &curve, SVGPathSink &sink) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | output_as (Curve const &curve, SVGPathSink &sink) |
| void | output_svg_path (Path &path, SVGPathSink &sink) |
| std::vector< std::vector< unsigned > > | sweep_bounds (std::vector< Rect > rs) |
| std::vector< std::vector< unsigned > > | sweep_bounds (std::vector< Rect > a, std::vector< Rect > b) |
| std::vector< std::vector< unsigned > > | fake_cull (unsigned a, unsigned b) |
| Matrix | operator* (Translate const &t, Scale const &s) |
| Matrix | operator* (Translate const &t, Rotate const &r) |
| Matrix | operator* (Scale const &s, Translate const &t) |
| Matrix | operator* (Scale const &s, Matrix const &m) |
| Matrix | operator* (Matrix const &m, Translate const &t) |
| Matrix | operator* (Matrix const &m, Scale const &s) |
| Point | operator* (Point const &v, Translate const &t) |
| Point | operator* (Point const &p, Scale const &s) |
| Point | operator* (Point const &v, Rotate const &r) |
| Matrix | operator* (Matrix const &m, Rotate const &r) |
| bool | logical_xor (bool a, bool b) |
| template<class T > | |
| int | sgn (const T &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | sqr (const T &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | cube (const T &x) |
| template<class T > | |
| const T & | between (const T &min, const T &max, const T &x) |
| double | round (double const x) |
| double | decimal_round (double const x, int const places) |
Variables | |
| const double | INV_EPS = (1L<<14) |
| const Coord | EPSILON = 1e-5 |
| const double | eps = .1 |
| const unsigned | MAXDEPTH = 64 |
| const double | BEPSILON = ldexp(1.0,((signed)-1)-MAXDEPTH) |
| unsigned | total_steps |
| unsigned | total_subs |
A convex cover is a sequence of convex polygons that completely cover the path. For now a convex hull class is included here (the convex-hull header is wrong)
Defines the different types of exceptions that 2geom can throw.
Copyright 2007 Johan Engelen goejendaagh@zonnet.nl
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it either under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License version 2.1 as published by the Free Software Foundation (the "LGPL") or, at your option, under the terms of the Mozilla Public License Version 1.1 (the "MPL"). If you do not alter this notice, a recipient may use your version of this file under either the MPL or the LGPL.
You should have received a copy of the LGPL along with this library in the file COPYING-LGPL-2.1; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA You should have received a copy of the MPL along with this library in the file COPYING-MPL-1.1
The contents of this file are subject to the Mozilla Public License Version 1.1 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.mozilla.org/MPL/
This software is distributed on an "AS IS" basis, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the LGPL or the MPL for the specific language governing rights and limitations.
two-dimensional geometric operators. Copyright 2007, JFBarraud Copyright 2007, njh
These operators are built on a more 'polynomially robust' transformation to map a function that takes a [0,1] parameter to a 2d vector into a function that takes the same [0,1] parameter to a unit vector with the same direction.
Rather that using (X/sqrt(X))(t) which involves two unstable operations, sqrt and divide, this approach forms a curve directly from the various tangent directions at each end (angular jet). As a result, the final path has a convergence behaviour derived from that of the sin and cos series. – njh
Various utility functions.
Copyright 2007 Johan Engelen goejendaagh@zonnet.nl Copyright 2006 Michael G. Sloan mgsloan@gmail.com
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it either under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License version 2.1 as published by the Free Software Foundation (the "LGPL") or, at your option, under the terms of the Mozilla Public License Version 1.1 (the "MPL"). If you do not alter this notice, a recipient may use your version of this file under either the MPL or the LGPL.
You should have received a copy of the LGPL along with this library in the file COPYING-LGPL-2.1; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA You should have received a copy of the MPL along with this library in the file COPYING-MPL-1.1
The contents of this file are subject to the Mozilla Public License Version 1.1 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.mozilla.org/MPL/
This software is distributed on an "AS IS" basis, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the LGPL or the MPL for the specific language governing rights and limitations.
| typedef double Geom::Coord |
A "real" type with sufficient precision for coordinates.
You may safely assume that double (or even float) provides enough precision for storing on-canvas points, and hence that double provides enough precision for dot products of differences of on-canvas points.
compute the angle turning from a to b. This should give 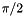 for angle_between(a, rot90(a)); This works by projecting b onto the basis defined by a, rot90(a)
for angle_between(a, rot90(a)); This works by projecting b onto the basis defined by a, rot90(a)
compute the angle turning from a to b (signed).
|
inline |
Between function - returns true if a number x is within a range. The values delimiting the range and the number must have the same type.
Fit a single-segment Bezier curve to a set of digitized points.
| int Geom::bezier_fit_cubic_full | ( | Point | bezier[], |
| int | split_points[], | ||
| Point const | data[], | ||
| int const | len, | ||
| Point const & | tHat1, | ||
| Point const & | tHat2, | ||
| double const | error, | ||
| unsigned const | max_beziers | ||
| ) |
Fit a multi-segment Bezier curve to a set of digitized points, without possible weedout of identical points and NaNs.
| max_beziers | Maximum number of generated segments |
| Result | array, must be large enough for n. segments * 4 elements. |
| int Geom::bezier_fit_cubic_r | ( | Point | bezier[], |
| Point const | data[], | ||
| int const | len, | ||
| double const | error, | ||
| unsigned const | max_beziers | ||
| ) |
Fit a multi-segment Bezier curve to a set of digitized points, with possible weedout of identical points and NaNs.
| max_beziers | Maximum number of generated segments |
| Result | array, must be large enough for n. segments * 4 elements. |
Evaluate a Bezier curve at parameter value t.
| degree | The degree of the Bezier curve: 3 for cubic, 2 for quadratic etc. Must be less than 4. |
| V | The control points for the Bezier curve. Must have (degree+1) elements. |
| t | The "parameter" value, specifying whereabouts along the curve to evaluate. Typically in the range [0.0, 1.0]. |
Let s = 1 - t. BezierII(1, V) gives (s, t) * V, i.e. t of the way from V[0] to V[1]. BezierII(2, V) gives (s**2, 2*s*t, t**2) * V. BezierII(3, V) gives (s**3, 3 s**2 t, 3s t**2, t**3) * V.
The derivative of BezierII(i, V) with respect to t is i * BezierII(i-1, V'), where for all j, V'[j] = V[j + 1] - V[j].
Pascal's triangle.
centroid using sbasis integration. This approach uses green's theorem to compute the area and centroid using integrals. For curved shapes this is much faster than converting to polyline.
Returned values: 0 for normal execution; 2 if area is zero, meaning centroid is meaningless.
Copyright Nathan Hurst 2006
| int Geom::centroid | ( | std::vector< Geom::Point > | p, |
| Geom::Point & | centroid, | ||
| double & | area | ||
| ) |
polyCentroid: Calculates the centroid (xCentroid, yCentroid) and area of a polygon, given its vertices (x[0], y[0]) ... (x[n-1], y[n-1]). It is assumed that the contour is closed, i.e., that the vertex following (x[n-1], y[n-1]) is (x[0], y[0]). The algebraic sign of the area is positive for counterclockwise ordering of vertices in x-y plane; otherwise negative.
Returned values: 0 for normal execution; 1 if the polygon is degenerate (number of vertices < 3); 2 if area = 0 (and the centroid is undefined).
for now we require the path to be a polyline and assume it is closed.
Estimate the (forward) tangent at point d[first + 0.5].
Unlike the center and right versions, this calculates the tangent in the way one might expect, i.e., wrt increasing index into d.
Estimate the (forward) tangent at point d[0].
Unlike the center and right versions, this calculates the tangent in the way one might expect, i.e., wrt increasing index into d.
Estimates the (backward) tangent at d[last].
|
inline |
Returns x rounded to the nearest places decimal places.
Implemented in terms of round, i.e. we make no guarantees as to what happens if x is half way between two rounded numbers.
Note: places is the number of decimal places without using scientific (e) notation, not the number of significant figures. This function may not be suitable for values of x whose magnitude is so far from 1 that one would want to use scientific (e) notation.
places may be negative: e.g. places = -2 means rounding to a multiple of .01
compute the euclidean distance between points a and b. TODO: hypot safer/faster?
compute the square of the distance between points a and b.
compute the dot product (inner product) between the vectors a and b.
Given a matrix m such that unit_circle = m*x, this returns the quadratic form x*A*x = 1.
Creates a Matrix given an axis and origin point. The axis is represented as two vectors, which represent skew, rotation, and scaling in two dimensions. from_basis(Point(1, 0), Point(0, 1), Point(0, 0)) would return the identity matrix.
| x_basis | the vector for the x-axis. |
| y_basis | the vector for the y-axis. |
| offset | the translation applied by the matrix. |
| ConvexHull Geom::graham_merge | ( | ConvexHull | a, |
| ConvexHull | b | ||
| ) |
if we modified graham scan to work top to bottom as proposed in lect754.pdf we could replace the angle sort with a simple merge sort type algorithm. furthermore, we could do the graham scan online, avoiding a bunch of memory copies. That would probably be linear. – njh
| bool Geom::is_zero | ( | Point const & | p | ) |
Returns true iff p is a zero vector, i.e. Point(0, 0).
(NaN is considered non-zero.)
Compute the square of L2 norm of p. Warning: this can overflow where L2 won't.
Given two points and a parameter t [0, 1], return a point proportionally from a to b by t. Akin to 1 degree bezier.
| IntersectorKind Geom::line_intersection | ( | Geom::Point const & | n0, |
| double const | d0, | ||
| Geom::Point const & | n1, | ||
| double const | d1, | ||
| Geom::Point & | result | ||
| ) |
Finds the intersection of the two (infinite) lines defined by the points p such that dot(n0, p) == d0 and dot(n1, p) == d1.
If the two lines intersect, then result becomes their point of intersection; otherwise, result remains unchanged.
This function finds the intersection of the two lines (infinite) defined by n0.X = d0 and x1.X = d1. The algorithm is as follows: To compute the intersection point use kramer's rule:
* convert lines to form * ax + by = c * dx + ey = f * * ( * e.g. a = (x2 - x1), b = (y2 - y1), c = (x2 - x1)*x1 + (y2 - y1)*y1 * ) * * In our case we use: * a = n0.x d = n1.x * b = n0.y e = n1.y * c = d0 f = d1 * * so: * * adx + bdy = cd * adx + aey = af * * bdy - aey = cd - af * (bd - ae)y = cd - af * * y = (cd - af)/(bd - ae) * * repeat for x and you get: * * x = (fb - ce)/(bd - ae)
If the denominator (bd-ae) is 0 then the lines are parallel, if the numerators are then 0 then the lines coincide.
| IntersectorKind Geom::line_twopoint_intersect | ( | Geom::Point const & | p00, |
| Geom::Point const & | p01, | ||
| Geom::Point const & | p10, | ||
| Geom::Point const & | p11, | ||
| Geom::Point & | result | ||
| ) |
Determine whether & where two line segments intersect.
If the two segments don't intersect, then result remains unchanged.
| double Geom::LInfty | ( | Point const & | p | ) |
Compute the L infinity, or maximum, norm of p.
|
inline |
A function to print out the Matrix (for debugging)
|
inline |
A function to print out the Point. It just prints out the coords on the given output stream
This is a lexicographical ordering for points. It is remarkably useful for sweepline algorithms
| Piecewise<T> Geom::partition | ( | const Piecewise< T > & | pw, |
| std::vector< double > const & | c | ||
| ) |
Piecewise<T> partition(const Piecewise<T> &pw, std::vector<double> const &c); Further subdivides the Piecewise<T> such that there is a cut at every value in c. Precondition: c sorted lower to higher.
//Given Piecewise<T> a and b: Piecewise<T> ac = a.partition(b.cuts); Piecewise<T> bc = b.partition(a.cuts); //ac.cuts should be equivalent to bc.cuts
| Piecewise<T> Geom::portion | ( | const Piecewise< T > & | pw, |
| double | from, | ||
| double | to | ||
| ) |
Piecewise<T> portion(const Piecewise<T> &pw, double from, double to); Returns a Piecewise<T> with a defined domain of [min(from, to), max(from, to)].
Returns p * Geom::rotate_degrees(90), but more efficient.
Angle direction in Inkscape code: If you use the traditional mathematics convention that y increases upwards, then positive angles are anticlockwise as per the mathematics convention. If you take the common non-mathematical convention that y increases downwards, then positive angles are clockwise, as is common outside of mathematics.
There is no rot_neg90 function: use -rot90(p) instead.
|
inline |
Returns x rounded to the nearest integer. It is unspecified what happens if x is half way between two integers: we may in future use rint/round on platforms that have them.
| IntersectorKind Geom::segment_intersect | ( | Geom::Point const & | p00, |
| Geom::Point const & | p01, | ||
| Geom::Point const & | p10, | ||
| Geom::Point const & | p11, | ||
| Geom::Point & | result | ||
| ) |
Determine whether & where two line segments intersect.
If the two segments don't intersect, then result remains unchanged.
|
inline |
Sign function - indicates the sign of a numeric type. -1 indicates negative, 1 indicates positive, and 0 indicates, well, 0. Mathsy people will know this is basically the derivative of abs, except for the fact that it is defined on 0.
Returns a version of a scaled to be a unit vector (within rounding error).
The current version tries to handle infinite coordinates gracefully, but it's not clear that any callers need that.